Lipase Gene Database (S. saprophyticus)
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus is a genus of gram positive cocci in cluster with 1µm in diameter. They are non motile, non spore forming, catalase positive and facultatively anaerobic. Staphylococcus saprophyticus are able to produce extracellular lipases which are lipoprotein in nature.
Lipase gene
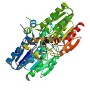 Staphylococcus saprophyticus lipase gene database comprises of lipase gene sequences and translation protein details. Lipase gene consists of Triacylglycerol esterase/lipase EstA domain and alpha/beta hydrolase fold which aid in lipid transport and metabolism. The catalytic apparatus of alpha/beta hydrolases typically involves three residues (catalytic triad): a serine, a glutamate or aspartate and a histidine, and often the mechanism involves a nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl carbon atom. Lipases are glycerol ester hydrolases that act on acylglycerols to liberate fatty acids and glycerol. Lipases can be divided into two main groups: (i) Carboxylesterases (EC 3.1.1.1) and (ii) “true” lipases (EC 3.1.1.3), which differ in several biochemical features. Staphylococcus lipases constitute a distinctive subfamily of microbial lipases that was named the lipase subfamilyI.5. All lipases are members of the α/β hydrolase fold super-family. Also, lipases share a conserved active site signature, the Gly-Xaa-Ser-Xaa-Gly motif
Staphylococcus saprophyticus lipase gene database comprises of lipase gene sequences and translation protein details. Lipase gene consists of Triacylglycerol esterase/lipase EstA domain and alpha/beta hydrolase fold which aid in lipid transport and metabolism. The catalytic apparatus of alpha/beta hydrolases typically involves three residues (catalytic triad): a serine, a glutamate or aspartate and a histidine, and often the mechanism involves a nucleophilic attack on a carbonyl carbon atom. Lipases are glycerol ester hydrolases that act on acylglycerols to liberate fatty acids and glycerol. Lipases can be divided into two main groups: (i) Carboxylesterases (EC 3.1.1.1) and (ii) “true” lipases (EC 3.1.1.3), which differ in several biochemical features. Staphylococcus lipases constitute a distinctive subfamily of microbial lipases that was named the lipase subfamilyI.5. All lipases are members of the α/β hydrolase fold super-family. Also, lipases share a conserved active site signature, the Gly-Xaa-Ser-Xaa-Gly motif